Understanding Wastewater Therapy Processes and Their Environmental Effect
The complexities of wastewater therapy processes play a crucial function in mitigating ecological challenges linked with water pollution. Each phase, from preliminary to sophisticated therapies, is developed to address certain contaminants, inevitably protecting both public wellness and water environments. However, regardless of technological advancements in therapy performance, significant obstacles persist, consisting of the administration of residual pollutants and the implications of nutrient drainage. As we explore the complexities of these processes, it ends up being essential to question how far present techniques can advance to meet the growing demands of sustainability and ecological preservation.
Overview of Wastewater Therapy
How is wastewater transformed right into a safe source for the setting? Wastewater treatment is an essential process developed to remove impurities from made use of water, consequently protecting public health and protecting ecosystems. This process starts with the collection of wastewater from property, industrial, and commercial resources, which is after that guided to treatment centers.
At these centers, different physical, chemical, and biological methods are employed to deal with the wastewater. Preliminary screening gets rid of big debris, adhered to by sedimentation to separate heavier solids. Ultimately, organic treatments, such as activated sludge procedures, make use of bacteria to break down organic issue. These techniques not only reduce toxin degrees but also facilitate the recuperation of beneficial nutrients.
The dealt with effluent can be safely discharged right into natural water bodies or reused for watering and industrial functions, advertising resource conservation. In addition, the treatment procedure produces biosolids, which can be repurposed as plant foods or soil changes, better improving sustainability.
Phases of Treatment Procedures
The wastewater therapy process typically is composed of 3 primary stages: initial, key, and secondary treatment. Each phase serves an unique duty in decreasing the contaminant load and making sure the effluent meets environmental requirements before discharge.
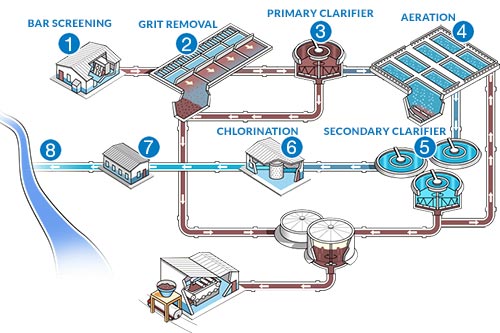
The primary therapy stage focuses on the physical splitting up of suspended solids from the wastewater. With sedimentation, much heavier fragments resolve at the end of sedimentation storage tanks, creating sludge, while lighter materials, such as oils and oils, float to the surface and are skimmed off. This process substantially lowers the natural and not natural tons in the wastewater.
Secondary therapy is an organic procedure targeted at further reducing the focus of natural matter. Numerous techniques, consisting of triggered sludge systems and trickling filters, make use of microorganisms to metabolize organic pollutants. This stage is crucial for achieving the required biochemical oxygen demand (FIGURE) decrease, ultimately causing cleaner effluent all set for discharge or further therapy. Each stage is vital in securing environmental and public health.
Advanced Treatment Technologies
Following the second therapy processes, advanced treatment modern technologies play an important role in more improving the quality of dealt with wastewater. These innovations are developed to remove recurring impurities that are not successfully eliminated throughout main and secondary therapies, making certain the effluent fulfills rigid regulatory standards.
Amongst the widely made use of innovative treatment approaches are membrane layer filtering, reverse osmosis, and advanced oxidation processes. Membrane purification, consisting of microfiltration and ultrafiltration, is efficient in separating great bits, microorganisms, and colloids from the water (Wastewater). Reverse osmosis uses semi-permeable membrane layers to get rid of dissolved solids, leading to high-grade water appropriate for various applications
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) use strong oxidants to degrade natural contaminants, including drugs and personal treatment products that are resistant to traditional treatment. These approaches boost the biodegradability of complicated compounds, facilitating their removal.
An additional significant modern technology is the use of biological nutrient elimination processes, which particularly target nitrogen and phosphorus, avoiding eutrophication in getting water bodies. Overall, sophisticated treatment modern technologies are vital for attaining higher degrees of purification, promoting water reuse, and securing public health while attending to the obstacles connected with wastewater administration.
Ecological Advantages of Therapy
Numerous environmental benefits arise from efficient wastewater therapy processes that contribute to ecosystem health and sustainability. Mainly, these procedures dramatically decrease the launch of dangerous contaminants into natural water bodies, which aids keep aquatic communities. By eliminating pollutants such as heavy steels, nutrients, and microorganisms, treated wastewater site link mitigates the threat of waterborne illness and promotes biodiversity in aquatic atmospheres.
Furthermore, wastewater treatment centers commonly employ innovative innovations that enable water recycling and reuse. This technique not just saves freshwater sources however additionally minimizes the demand on natural water products. Improved nutrient removal from wastewater can also prevent eutrophication, a procedure that try this out causes algal blooms and succeeding oxygen exhaustion in aquatic systems.
In addition, reliable therapy procedures can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane and laughing gas, which are frequently released throughout unattended wastewater disintegration. By recording and using biogas from anaerobic digesters, facilities can transform waste into renewable resource, thereby adding to a reduction in fossil gas dependency.
Obstacles and Future Patterns
While the ecological advantages of wastewater treatment are clear, a number of challenges continue that prevent optimum outcomes in this area. One significant issue is aging facilities, which often causes inadequacies and enhanced functional prices - Wastewater. Numerous treatment plants were made decades ago, and their abilities do not straighten with modern needs, which consist of stricter regulative requirements and greater volumes of wastewater due to urbanization

Looking ahead, there is a growing emphasis on source recuperation and round economy principles within wastewater treatment. Developments such as anaerobic food digestion, which can generate biogas, and progressed purification technologies are obtaining grip. These methods not just boost treatment effectiveness yet likewise promote sustainability.
Ultimately, addressing these obstacles needs collaboration amongst stakeholders, financial investment in innovation, and a commitment to ongoing study. By accepting these trends, the wastewater therapy industry can evolve to fulfill the demands of a changing setting and society.
Conclusion
In verdict, wastewater treatment processes click this link play an essential role in improving ecological quality and public health and wellness. The multi-stage therapy framework, paired with advanced innovations, effectively minimizes pollution and promotes lasting water management.